
I Research : Journal of Pharmacy
The I Research : Journal of Pharmacy provides a resource content about Pharmacy field especially about the community pharmacy, dispensing pharmacy, Pharmacovigilance etc. This journal aims to publish all the recent research and reviews articles related to pharmacy like the pharmaceutical dosage forms, community and dispensing pharmacy, Clinical pharmacy, Incompatibility in dosage forms and regulations in pharma business etc. It is the international journal of published Bi-Annual by I ResearchAcademia. Authors should consult the latest instructions to authors before preparing their manuscripts. All contributions must be in English and should be submitted online only in a single word file.
Current Issue: I Research: Journal of Pharmacy July - Dec 2025
Volume 3, Number 2 (2025)
Design, Development and Stability Optimization of Targeted Doxorubicin-Loaded Liposomes
By N.Preethi , Dr.M.Amudha , P.Santhiya , Dr.V.Ganesan
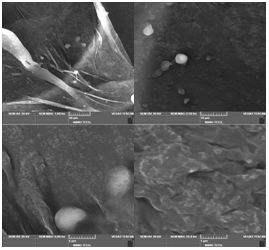
The present study aimed to formulate and evaluate a doxorubicin-loaded liposomal drug delivery system to enhance therapeutic efficacy and minimize systemic toxicity. Doxorubicin, a potent chemotherapeutic agent, is widely used in the treatment of various cancers; however, its clinical utility is limited by dose- dependent cardio toxicity and poor tumor selectivity. To overcome these drawbacks, liposomal encapsulation was explored as an advanced nanocarrier system to achieve targeted and sustained drug delivery. Preformulation studies were carried out to assess the compatibility between the drugandexcipientsusingstandardanalyticaltechniques,confirmingnosignificant interactions. Liposomes were successfully prepared using the thin-film hydration method followed by sonication to achieve nanosized vesicles. The optimized formulation was characterized for particle size, polydispersity index (PDI), zeta potential, surface morphology, encapsulation efficiency, and in-vitro drug release profile. The liposomal vesicles exhibited an average particle size of 125–160 nm, low PDI indicating uniformity, high encapsulation efficiency (78–88%), spherical morphology under microscopic observation, and a favorable zeta potential greater than –25 mV, signifying good stability. In-vitro drug release studies displayed a biphasic pattern characterized by an initial burst release followed by a sustained release phase, influenced by lipid composition. Stability studies confirmed that the liposomal formulation remained stable at 4°C for 15 days, indicating suitable storage conditions. Overall, the study demonstrates that liposomal encapsulation of doxorubicin can significantly enhance its therapeutic index by prolonging circulation time, improving tumor targeting through the Enhanced Permeability and Retention (EPR) effect, and reducing systemic toxicity. These results provide a strong foundation for further in-vivo studies and potential clinical translation.

Encapsulation of Phyllanthus Emblica Fruit Extract Biodegarable Gelatin Nanosperes: Design Characterization and In Vitro Antioxidant Assessment
By jeeva .E, P.Santhiya , Dr.M.Amudha , Dr.V.Ganesan
Neurodegenerative disorders represent a class of progressive diseases that lead to irreversible loss of neuronal function within the brain and central nervous system. Among them, Huntington’s disease (HD) is a fatal neuropsychiatric condition, with its prevalence in India comparable to that observed in Western populations. Despite significant advances in research, no effective curative therapy exists to arrest or reverse disease progression. A major challenge in HD management lies in the restricted permeability of therapeutic agents across the blood–brain barrier (BBB), which limits drug availability within the central nervous system. Moreover, conventional pharmacological treatments are often associated with adverse systemic effects. In the present investigation, an attempt was made to develop Phyllanthus emblica extract–loaded gelatin nanospheres as a novel nanoformulation for potential use in the treatment of Huntington’s disease. Pre-formulation studies were carried out to determine the solubility and physicochemical characteristics of the extract. FTIR and UV analyses confirmed the absence of drug–polymer interactions, showing a distinct absorption peak at 273 nm. The nanospheres (formulations F1–F4) were prepared by the solvent displacement method and evaluated for particle size, surface morphology, zeta potential, entrapment efficiency, and drug loading. Entrapment efficiency values ranged from 40.61% to 80.21%, while drug loading varied between 18.79% and 50.33%. Among all, formulation F2 exhibited optimal characteristics with a sustained drug release profile, showing 10% release at 1 hour and 37% release at 6 hours. The antioxidant potential of the nanospheres was further assessed by DPPH assay, revealing strong free radical scavenging activity. Overall, the results indicate that Emblica officinalis–loaded gelatin nanospheres may serve as an effective, biocompatible nanocarrier for targeted brain delivery in the management of Huntington’s disease. Further in vivo investigations and optimization are warranted to establish their therapeutic efficacy and clinical relevance.
Artificial Intelligence in Drug Interactions and Adverse Drug Reaction Analysis: Current Trends and Applications
By S MOHAMED MUSAMIL
Background: Negative responses to pharmaceutical agents (ADRs) represent a critical global health issue, contributing significantly to morbidity, mortality, and patient discomfort. Conventional drug safety monitoring largely depends on traditional data submission systems, which are frequently hampered by reporting delays, incomplete information, and underreporting. The integration of advanced computational intelligence (AI) offers a transformative solution to enhance the precision, efficiency, and responsiveness of ADR surveillance. Objective: This review seeks to assess the present landscape of AI applications in monitoring ADRs and to examine its potential to revolutionize pharmacovigilance practices. Methods: An extensive literature survey was undertaken using databases such as PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science, focusing on studies conducted between 2015 and 2025 that employed AI methodologies for ADR detection. In addition, a prototype software application was developed to analyze drug-related ADRs using AI-based input interpretation. Results: AI models, particularly those utilizing automated learning algorithms and computational linguistic modeling, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in identifying ADRs within large-scale biomedical data. Evidence suggests that AI can uncover latent patterns in electronic clinical records, extract relevant insights from social media, and facilitate automated risk signal identification in pharmacovigilance systems. Nevertheless, challenges related to data inconsistency, lack of standardized frameworks, and ethical considerations persist. Conclusion: AI has the potential to significantly advance real-time, proactive drug safety monitoring. Although initial outcomes are promising, broader adoption will require further clinical validation, regulatory alignment, and the establishment of comprehensive ethical guidelines.
News & Announcements
There are no news or announcements at this time.
